Page: 2
10. Java.lang Package
Q: 06 Given: 11. public static void test(String str) {
12. int check = 4;
13. if (check = str.length()) {
14. System.out.print(str.charAt(check -= 1) +", ");
15. } else {
16. System.out.print(str.charAt(0) + ", ");
17. }
18. }
and the invocation:
21. test("four");
22. test("tee");
23. test("to");
What is the result?
A. r, t, t,
B. r, e, o,
C. Compilation fails.
D. An exception is thrown at runtime.
Answer: C Q: 07 Given: 11. public class Person {
12. private String name;
13. public Person(String name) {
14. this.name = name;
15. }
16. public boolean equals(Object o) {
17. if ( ! o instanceof Person ) return false;
18. Person p = (Person) o;
19. return p.name.equals(this.name);
20. }
21. }
Which statement is true? A. Compilation fails because the hashCode method is not overridden.
B. A HashSet could contain multiple Person objects with the same name.
C. All Person objects will have the same hash code because the hashCode method is not overridden.
D. If a HashSet contains more than one Person object with name="Fred", then removing another Person, also
with name="Fred", will remove them all. Answer: B Q: 08 Which two statements are true about the hashCode method? (Choose two.) A. The hashCode method for a given class can be used to test for object equality and object inequality for that
class.
B. The hashCode method is used by the java.util.SortedSet collection class to order the elements within that set.
C. The hashCode method for a given class can be used to test for object inequality, but NOT object equality, for
that class.
D. The only important characteristic of the values returned by a hashCode method is that the distribution of
values must follow a Gaussian distribution.
E. The hashCode method is used by the java.util.HashSet collection class to group the elements within that set
into hash buckets for swift retrieval.
Answer: C, E
Q: 09 Click the Task button.
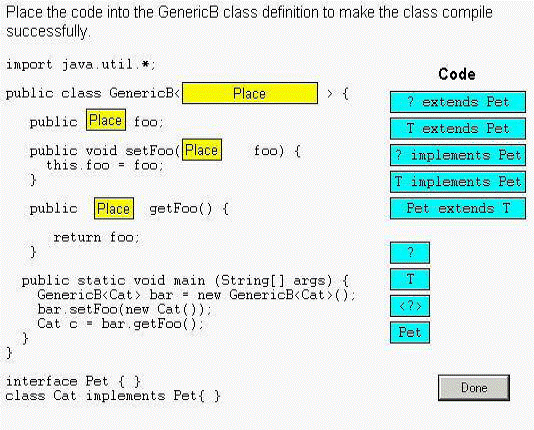 1.<T extends Pet>
2. T
3.T
4.T
Q: 10 Given:
10. public class MyClass {
11.
12. public Integer startingI;
13. public void methodA() {
14. Integer i = new Integer(25);
15. startingI = i;
16. methodB(i);
17. }
18. private void methodB(Integer i2) {
19. i2 = i2.intValue();
20.
21. }
22. }
If methodA is invoked, which two are true at line 20? (Choose two.)
A. i2 == startingI returns true.
B. i2 == startingI returns false.
C. i2.equals(startingI) returns true.
D. i2.equals(startingI) returns false.
Answer: B, C
Page: 2
1
2
3
|